Today I’m here to offer more SEO and foreign trade efficiency – enhancing tips. Specifically, we’ll focus on advanced search commands in Google.
Many colleagues and friends struggle to get precise results from Google’s vast database. They mainly rely on basic keyword searches. While some SEO pros use the “site:” command for checking indexing, they seldom utilize other advanced commands. So, let’s explore these commands and their functions.
I. Logical Operators: The Smart Hub for Precise Search Results
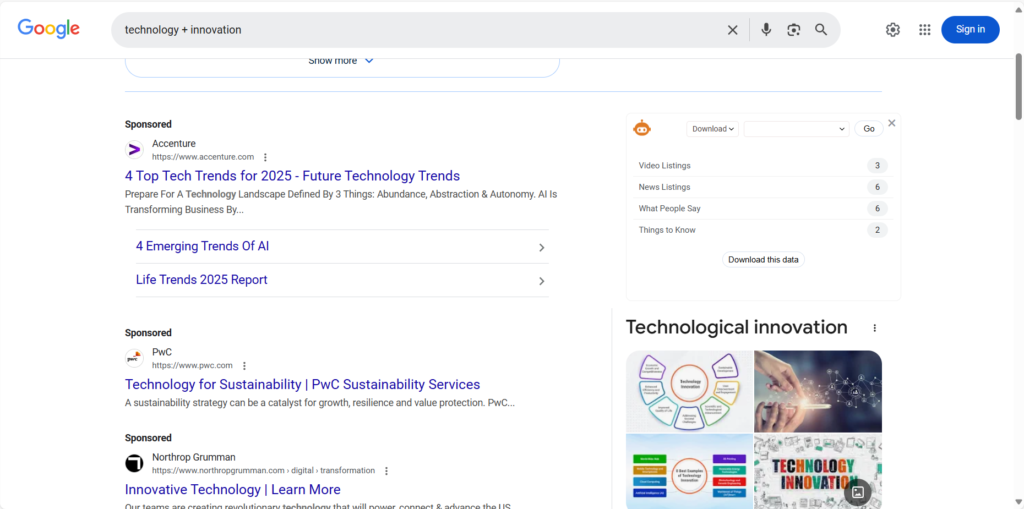
1. “+” Command: Precise Matching
The “+” in Google search acts as a strict filter. It ensures that search results contain all specified keywords. For example, when you type “technology + innovation”, Google will only show pages with both “technology” and “innovation”, helping you quickly access the latest in tech innovation, be it AI breakthroughs or new energy tech.
2. “-” Command: Filtering Out Irrelevant Info
The “-” is like a precise scalpel. Searching “apple – phone” will exclude iPhone – related pages, leaving only info about apples as fruit or Apple Inc.’s non – phone – related news, allowing you to avoid distractions and find the exact information you need.
3. “OR” Command: Expanding Search Horizons
The “OR” command is a key to multiple information doors. Searching “novel OR biography” will display pages related to either novels or biographies, such as “One Hundred Years of Solitude” or “The Biography of Su Dongpo”, greatly expanding your reading exploration.
II. Quotation Marks and Wildcards: The Magic Brushes for Customized Searches
1. Double Quotation Marks “”
Double quotation marks ensure exact keyword matching. Typing “‘Harry Potter and the Philosopher’s Stone’” will return only relevant info about this classic, like book details, movie news, and fan comments, leading you straight to the heart of the “Harry Potter” magic world.
2. Wildcard *
The asterisk (*) is a creative exploration tool for fuzzy matching. Searching “science fiction movie” might bring up “science fiction adventure movie” and other variations, helping you discover niche but exciting sci – fi movies and their unique concepts.
III. Specific – Domain Commands: Secret Weapons for Professional Searches
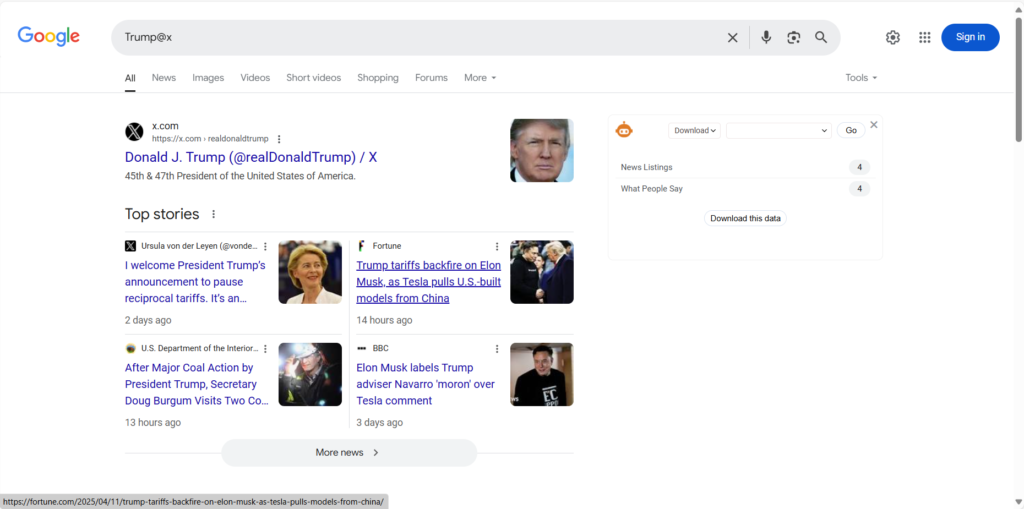
1. “@” Command: Social Media Tracking
The “@” command is a compass for social media searches. Typing “Trump@x” will gather all Trump’s tweets and interactions on Twitter. It can help find clients on social media, scout for overseas influencers, or identify SEO website authors.
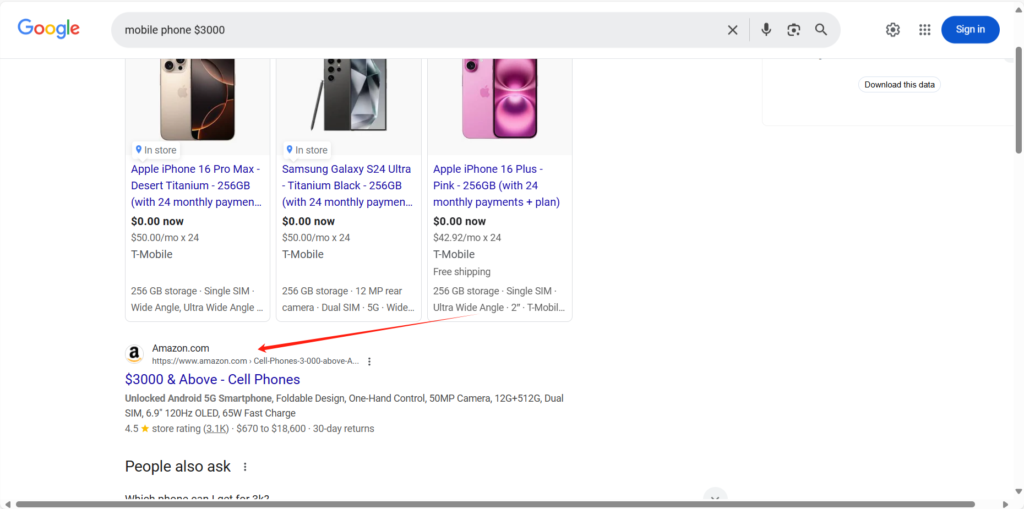
2. “$” Command: Price – Based Search
The “$” command is a price detector for shoppers. Searching “mobile phone $3000” helps you find phones within that price range, narrowing down search results for more accurate shopping.
3. “filetype” Command: File Search
The “filetype” command is a pro at finding specific files. Searching “English grammar filetype:ppt” will retrieve relevant PPTs for English grammar learning, from basic to advanced, making English study more efficient.
4. “site” Command: Site – Specific Search
The “site” command, often used by SEOs for indexing checks, can also explore specific websites. For example, “photography skills site:blog.cn” will search for photography skills content on blog.cn. SEOs can use it to find relevant content on high – quality sites for link – building. Note that site results may not reflect actual indexing, and continuous failure to site a URL may indicate issues.
IV. Web Element Search Commands: Precise Compasses for Information Location
1. “cache” Command: Deprecated, New Alternatives
The “cache” command, once used to view past web page versions, is no longer supported by Google. Now, use Google Search Console (GSC) for your own site’s cache or archive.org for any site. A newer cache date usually

means higher Google attention and more frequent crawling.
2. “related” Command: Discovering Related Sites
The “related” command connects you to related websites. Searching “related: Douban Movies” will lead you to similar movie – related sites, expanding your movie – exploration horizons.
3. “link” Command: Link Tracing
The “link” command traces links to a specific URL. Searching “link:shein.com” will show all indexed links pointing to shein.com, both internal and external, helping you understand the site’s network relationships.
4. “inurl” Command: URL Detection
The “inurl” command helps find websites through partial URL searches. For example, using part of a SHEIN URL with “inurl” can locate the corresponding product page, as long as it’s indexed by Google.
5. “intitle” Command: Title – Focused Search
The “intitle” command highlights pages with specific keywords in their titles. Searching “intitle: travel recommendation” will quickly show travel – related pages with this in their titles, offering valuable travel tips.
6. “intext” Command: Text – Based Search
The “intext” command digs into page text. Searching “novel recommendation intext: romance” will find novel recommendations with “romance” in the text, great for literature lovers.
7. “inanchor” Command: Anchor Text Tracking
The “inanchor” command locates pages with specific anchor text. Searching “inanchor: fitness course” will show pages related to fitness courses, useful for fitness enthusiasts.
V. Command Combinations: The Ultimate Secret of Super Searching
1. Academic Research
For academic research, commands like “‘AI:pdf site:edu.cn” can unearth AI – related PDF papers from educational institutions, providing in – depth academic insights for researchers. Using such commands to find academic references can make AI – written content more rigorous.
2. Shopping
During shopping, “brand name model $ budget intext: review site: e – commerce platform.com” helps consumers find product reviews within their budget, making informed purchasing decisions.
3. Literary Exploration
In literary exploration, “‘Haruki Murakami’ intitle: work appreciation site: literature forum.net” can find in – depth analyses of Murakami’s works on literature forums, enriching readers’ understanding of his works.