Methods for Querying the Number of Pages Indexed by Google
1. Using the site: Operator
The site: operator is a quick and straightforward way to estimate the number of pages indexed by Google for a specific domain. Here’s how it works:
- Enter
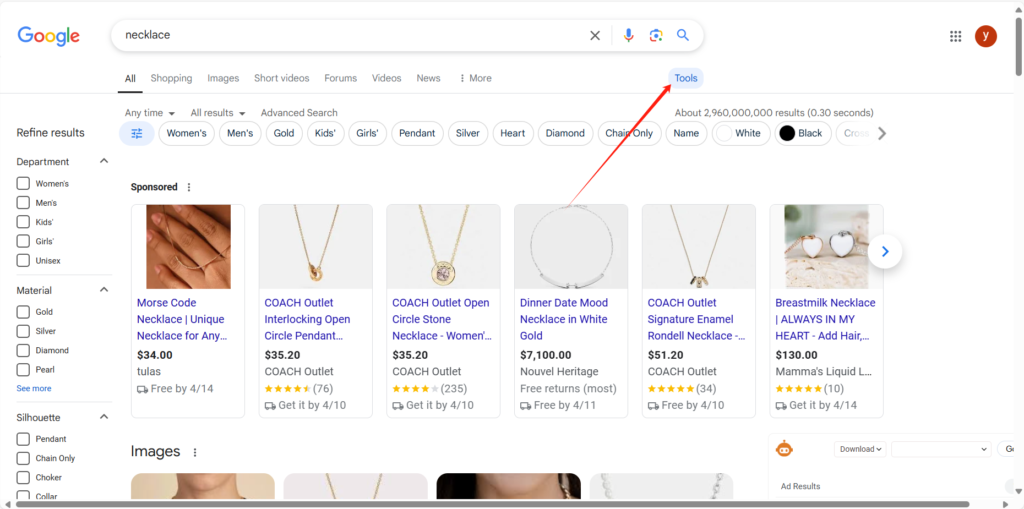
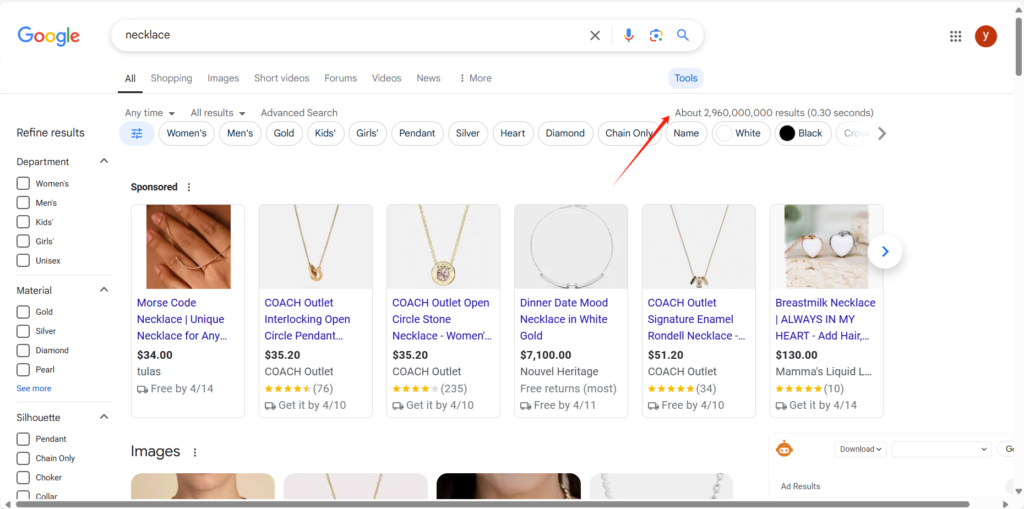
site:yourwebsite.com(replaceyourwebsite.comwith your domain) in the Google search bar. - If the website is indexed, Google will display results from that domain. Previously, the number of results was shown directly on the search results page. Now, you may need to click on [Tools] (or [Tool] in the English interface) to view the approximate number of indexed pages 1 2.
- This method can also be used to check competitors’ websites.
Limitations:
- The
site:operator provides an approximate count and may include duplicate URLs, cached pages, or pages that are not officially indexed. - It can display up to approximately 1,000 results due to pagination limitations.
2. Using Google Search Console (GSC)
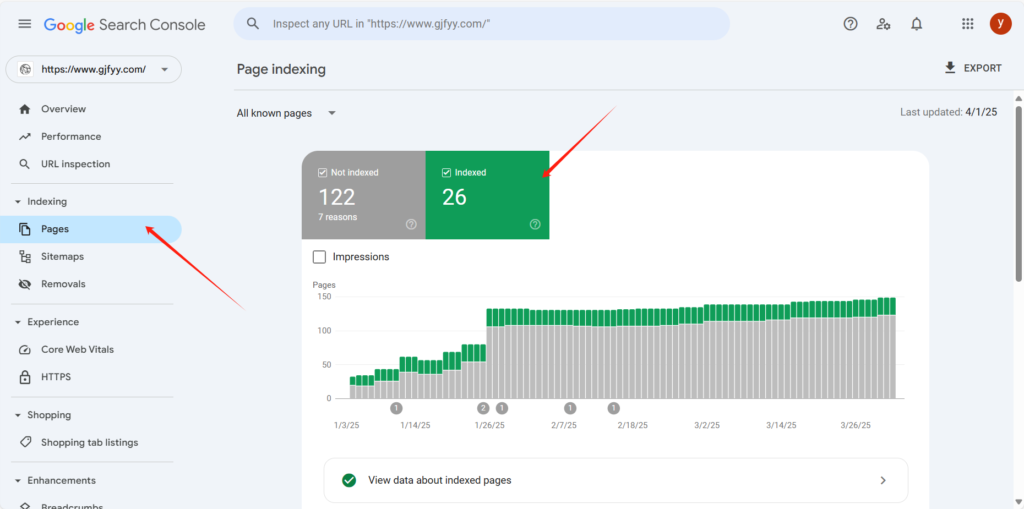
Google Search Console offers a more accurate and detailed way to check the indexing status of your website:
- Log in to GSC and navigate to the Coverage report.
- This report shows the exact number of indexed pages, along with details about excluded pages and any technical issues 3.
- GSC also highlights pages blocked by
robots.txt, marked asnoindex, or affected by JavaScript rendering issues.
Limitations:
- GSC can only be used for websites you own or have access to (ownership verification is required).
- It does not provide data for competitors’ websites.
Key Differences Between the Two Methods
| Aspect | site: Operator | Google Search Console (GSC) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Quick estimation of indexed pages for any domain | Detailed analysis of your own website’s indexing status |
| Returned URLs | May include duplicate URLs, cached pages, or non-indexed pages | Only includes officially indexed pages (canonical URLs) |
| Result Sorting | Results are sorted by Google’s relevance algorithm | Provides a structured report with technical insights |
| Usage Scenarios | Suitable for checking competitors’ websites or quick checks | Best for in-depth analysis of your own website |
| Limitations | Limited to ~1,000 results; affected by caching and personalization | Requires ownership verification; cannot analyze competitors |
Reasons for Inconsistencies Between GSC and the site: Operator
- Data Sources and Update Frequencies:
- GSC data is based on Google’s index database and may have a 1-3 day delay.
- The
site:operator shows real-time results but is influenced by caching, personalization, and algorithmic filtering.
- Index Status and Exclusion Mechanisms:
- GSC includes only valuable, officially indexed pages and excludes problematic ones.
- The
site:operator may display non-indexed or hidden pages.
- Pagination and Result Truncation:
- The
site:operator is limited to ~1,000 results, while GSC provides the exact count.
- The
- URL Normalization and Duplicate Content:
- GSC counts only canonical URLs, while the
site:operator may show duplicates.
- GSC counts only canonical URLs, while the
- Technical Limitations:
- GSC flags pages blocked by
robots.txtor marked asnoindex, while thesite:operator may show cached versions of such pages.
- GSC flags pages blocked by
- Scope of Property Verification:
- GSC requires ownership verification and provides data only for verified properties.
- The
site:operator may mix results from different subdomains or protocol versions (e.g., HTTP vs. HTTPS).